Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yokoyama, Sumi; Noguchi, Hiroshi; Ichimasa, Yusuke*; Ichimasa, Michiko*
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 71(3), p.201 - 213, 2004/01
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:22.49(Environmental Sciences)The reemission process of tritiated water (HTO) deposited on a soil surface is an important process to assess tritium doses to the general public around nuclear fusion facilities. A field experiment using heavy water (HDO) as a substitute for HTO was curried out in the summertime to investigate the reemission process of HTO from soil to the atmosphere. In the experiment, the time variations of the depth profiles of HDO concentrations in soil exposed to HDO vapour and soil mixed with HDO were measured during the reemission process on the field. The decrease of HDO concentration insoil water of exposed soil was much greater than that of mixed soil. The reemission process was analysed using a model including the evaporation of HDO from soil, the exchange between the soil HDO and air H O, and the diffusion of HDO in soil. It was found that the model is applicable to calculating the time variations of detailed depth profiles of HDO concentration in soil water in surface soil layers.
O, and the diffusion of HDO in soil. It was found that the model is applicable to calculating the time variations of detailed depth profiles of HDO concentration in soil water in surface soil layers.
 C,
C,  Cs and stable carbon composition in forest soil and its implications
Cs and stable carbon composition in forest soil and its implicationsGuo, J.; Atarashi-Andoh, Mariko; Amano, Hikaru
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 255(1), p.223 - 229, 2003/01
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:45.77(Chemistry, Analytical)Soil organic matter content, 
 C,
C,  C and
C and  Cs radioactivity were determined in 3 undisturbed forest soil profiles in Ibaraki prefecture, Japan to estimate
Cs radioactivity were determined in 3 undisturbed forest soil profiles in Ibaraki prefecture, Japan to estimate  C migration in surface environment. The
C migration in surface environment. The  Cs data illustrate that no disturbance has occurred during past years in 3 soil profiles. The peak values are observed in the top 10 cm of the soil profiles.
Cs data illustrate that no disturbance has occurred during past years in 3 soil profiles. The peak values are observed in the top 10 cm of the soil profiles.  C activities were determined with fast bomb combustion-liquid scintillation counting method.
C activities were determined with fast bomb combustion-liquid scintillation counting method.  C determination shows that
C determination shows that  C also has peak values in the top 10 cm of the soil profiles ascribed to the highest bomb
C also has peak values in the top 10 cm of the soil profiles ascribed to the highest bomb  C level in 1960's.
C level in 1960's.
 C values continuously decreased with increasing soil depth. Enrichment of deeper soils in isotope ratio probably results from discrimination against
C values continuously decreased with increasing soil depth. Enrichment of deeper soils in isotope ratio probably results from discrimination against  C during mineralization and loss of isotopically lighter carbon from soils due to root uptake, leaching etc.It shows that
C during mineralization and loss of isotopically lighter carbon from soils due to root uptake, leaching etc.It shows that 
 C is an excellent indicator of soil carbon turnover and belowground process.
C is an excellent indicator of soil carbon turnover and belowground process.
Jiang, Q.*; Tamura, Kenji*; Asano, Maki*; Fukuyama, Kenjin*; Yamaji, Keiko*
no journal, ,
This study was conducted to understand the soil macro and micromorphological characteristics on the former open pit mining area of Ningyo-toge mine. The vegetation succession of the area has not progressed. Its dominant vegetation has been 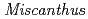 . The conclusions of this study are follows. The BC horizon of Site B has a lower Eh, which may be due to the less voids in the underlying soil, which results in seasonal accumulation of water. The contents of Mn, Cd, Pb, and Co were higher than the average contents in Japanese soil, but they did not reach the level of pollution. The content of acid-soluble Fe was very low in the soil, Fe mainly is the form of residual and a part of reducible form in the study site. But, the content of Mn in acid-soluble form is high, and Mn has a greater impact on vegetation. In this study site, external human factors have a large influence, mixed with a large amount of black residue and wood chips. And the 0-5cm of soil is in good structure, but the soil in the lower layer is not fully developed and it is a block structure.
. The conclusions of this study are follows. The BC horizon of Site B has a lower Eh, which may be due to the less voids in the underlying soil, which results in seasonal accumulation of water. The contents of Mn, Cd, Pb, and Co were higher than the average contents in Japanese soil, but they did not reach the level of pollution. The content of acid-soluble Fe was very low in the soil, Fe mainly is the form of residual and a part of reducible form in the study site. But, the content of Mn in acid-soluble form is high, and Mn has a greater impact on vegetation. In this study site, external human factors have a large influence, mixed with a large amount of black residue and wood chips. And the 0-5cm of soil is in good structure, but the soil in the lower layer is not fully developed and it is a block structure.